Crystallization According to Nakamura
Crystallization according to Nakamura is the crystal growth model for non-isothermal crystallization kinetics during cooling.
Nakamura equation is found as the integral form of isothermal Avrami nucleation under the assumption that the non-isothermal kinetics during cooling can be explained using a series of infinitesimal steps with isothermal Avrami nucleation.
Generally, the crystallization rate can be written as a product of two functions, where the first one f(α) depends on crystallization degree α and the second one K(T) depends on temperature.
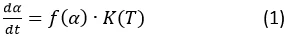
f(α) is the reaction type according to Avrami nucleation with dimension n
f(α)=n*(1- α)*[-ln(1- α)](n-1)/n (2)
If temperature dependence K(T) is known then for cooling rate β the degree of crystallization α can be found according to Nakamura equation:
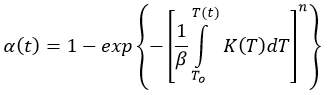
Nowadays, for analytical dependence K(T) the Hoffman-Lauritzen theory is used.
Reference
NAKAMURA, K., WATANABE, T., KATAYAMA, K., AMANO, T., Some aspects of non-isothermal crystallization of polymers — Part I: Relationship between crystallization temperature, crystallinity and cooling conditions, Journal of Applied Polymer Science, Vol. 16, pp. 1077-1091, 1972